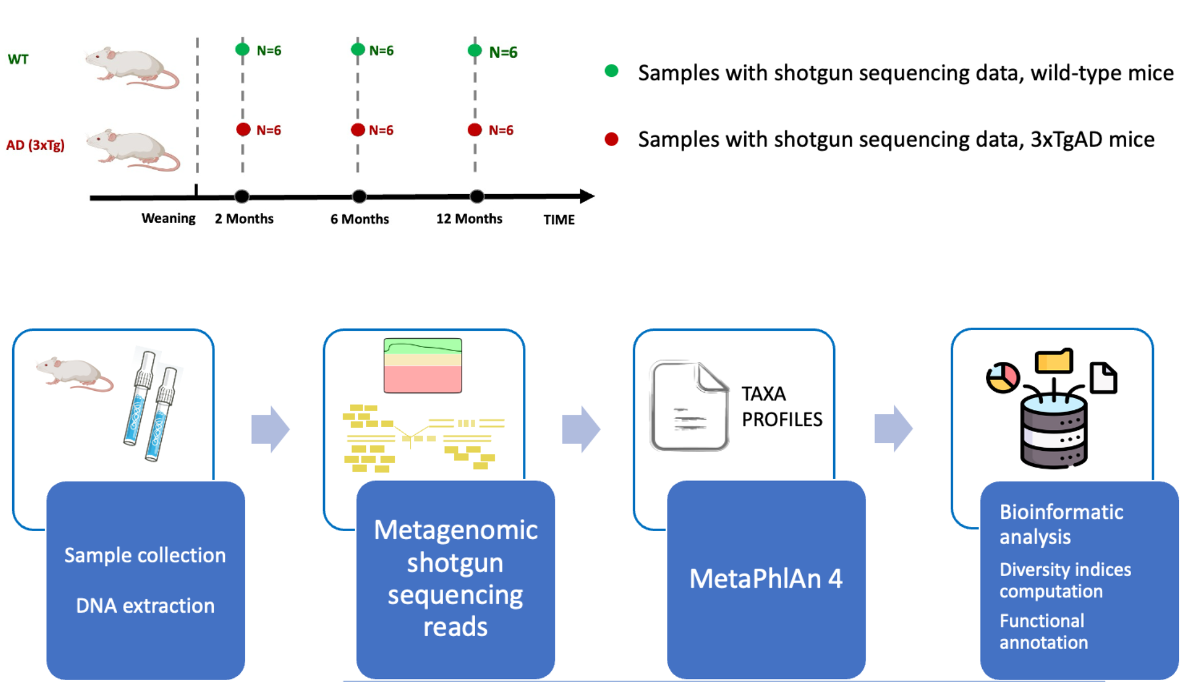
We are excited to announce the publication of our latest research exploring the complex relationship between Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and gut microbiota. Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that significantly impairs cognitive functions, memory, and physical abilities. Understanding its progression and underlying mechanisms is crucial for developing effective interventions. In our study, we performed shotgun metagenomics sequencing on 3xTgAD mice at key stages of AD progression—specifically at 2, 6, and 12 months of age. By collecting and analyzing fecal samples from both 3xTgAD and wild-type mice, we aimed to characterize how the gut microbiota modulates in an in vivo AD model over time. Utilizing MetaPhlAn 4 for quantitative taxon abundance assessment, we ensured a precise representation of the microbial communities present. Our analysis focused on species-level genome bins (SGBs), including both known (kSGBs) and unknown (uSGBs) species, as well as higher taxonomic categories like family-level (FGBs), class-level (CGBs), and order-level genome bins (OGBs). Key Findings: • Extensive Gut Microbial Diversity: AD mice exhibited a wide range of gut microbial species, indicating significant diversity compared to wild-type mice. • Significant Changes in Bacteroidota and Firmicutes Phyla: The most notable microbiome changes associated with AD and aging were found within SGBs belonging to the Bacteroidota and Firmicutes phyla. • Presence of Uncharacterized Species: A substantial set of uncharacterized SGBs was identified, emphasizing the need for further research to understand their roles. Our findings highlight the importance of advanced bioinformatic studies to accurately classify and analyze these elusive microbial species. Understanding these microbes could shed light on their potential role in the gut-brain axis and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. We believe this research opens new avenues for exploring how gut microbiota influences neurodegenerative diseases and could lead to novel therapeutic strategies. We invite you to read the full paper to delve deeper into our research and join the conversation on this critical topic. Stay tuned for more updates!
New Study Unveils Gut Microbiota Changes in Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model